Access Database for CRM: 7 Ultimate Power Tips to Master Data
Ever wondered how top businesses keep customer relationships strong and sales soaring? The secret often lies in a well-structured access database for CRM. It’s not just about storing names and emails—it’s about turning data into strategy, one record at a time.
1. Understanding Access Database for CRM: The Foundation

At its core, an access database for CRM is a centralized system that allows businesses to store, manage, and analyze customer information efficiently. Microsoft Access, while not a full-scale enterprise solution like SQL Server or Oracle, offers a user-friendly interface that makes it ideal for small to mid-sized businesses looking to build a custom CRM system without heavy IT investment.
What Is an Access Database?
Microsoft Access is a relational database management system (RDBMS) included in the Microsoft Office suite. It combines the Access Database Engine (formerly Jet Database Engine) with a graphical user interface and software development tools. Unlike spreadsheets, Access allows for structured data storage using tables, queries, forms, and reports—making it a powerful tool for managing complex datasets.
- Stores data in tables with defined relationships
- Supports queries to extract meaningful insights
- Enables form creation for easy data entry
Why Use Access for CRM?
While enterprise CRM platforms like Salesforce or HubSpot dominate the market, many small businesses find them costly or overly complex. An access database for CRM provides a cost-effective alternative. You can customize fields, automate workflows, and generate reports without relying on third-party subscriptions.
“Access gives you the power to build a CRM tailored to your business, not the other way around.” — TechRadar Database Review
Common Use Cases
Small sales teams, non-profits, and startups often use Access databases to track leads, manage client interactions, and monitor follow-ups. For example, a local real estate agency might use Access to log property viewings, client preferences, and agent notes—all within a single, searchable database.
- Lead tracking and follow-up scheduling
- Customer service history logging
- Sales pipeline visualization
2. Benefits of Using Access Database for CRM
Choosing an access database for CRM isn’t just about saving money—it’s about gaining control. When you own your data structure, you can adapt quickly to changing business needs. Let’s explore the key advantages that make Access a compelling choice.
Cost-Effectiveness
One of the biggest draws of using Access is its affordability. If you already have Microsoft Office, Access is likely included at no extra cost. Compare that to monthly SaaS CRM subscriptions, which can run into hundreds or even thousands of dollars per year for a small team.
- No recurring subscription fees
- Minimal hardware requirements
- Reduced dependency on external vendors
Customization and Flexibility
Unlike off-the-shelf CRM software, Access lets you design your database exactly how you need it. Want to add a field for “Preferred Contact Time” or “Pet Ownership” for a pet supply business? You can do that in minutes. This level of customization is hard to match with pre-built CRM tools.
With VBA (Visual Basic for Applications), you can even automate tasks like sending email reminders or updating status fields based on user input. This flexibility makes an access database for CRM a dynamic tool that evolves with your business.
User-Friendly Interface
Access uses a familiar interface for anyone who’s used Excel or Word. Forms can be designed to look like simple data entry screens, making it easy for non-technical staff to use. Reports can be generated with a few clicks, and queries can be built using a visual query designer—no SQL knowledge required.
“Access lowers the barrier to database management, empowering teams to take ownership of their data.” — Microsoft Official Documentation
3. Key Components of an Access Database for CRM
To build an effective CRM system in Access, you need to understand its core components. Each plays a vital role in how data is stored, accessed, and presented.
Tables: The Backbone of Your CRM
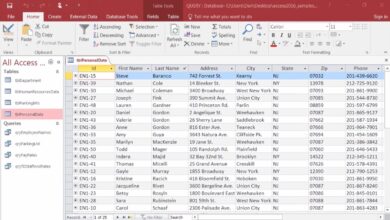
Tables are where all your data lives. In a CRM context, you’ll typically have tables for customers, contacts, interactions, leads, and products. Each table consists of fields (columns) and records (rows). For example, a Customers table might include fields like CustomerID, Name, Email, Phone, and LastContactDate.
- Define primary keys to uniquely identify records
- Use data types appropriately (e.g., Date/Time for follow-ups)
- Set validation rules to ensure data accuracy
Queries: Extracting Intelligence from Data
Queries allow you to retrieve specific data based on criteria. For instance, you can create a query to find all customers who haven’t been contacted in the last 30 days. This is crucial for proactive customer engagement.
You can use the Query Design view to build queries without writing code. For more advanced users, SQL view offers full control. Queries can also join multiple tables—like linking a customer to their recent purchases or support tickets.
Forms and Reports: User Interaction and Output
Forms make data entry intuitive. Instead of editing raw table data, users can fill out a form that looks like a digital business card. Reports, on the other hand, turn data into professional-looking documents for printing or sharing. You can generate monthly sales reports, customer activity summaries, or lead conversion rates.
- Use forms to reduce data entry errors
- Design reports with branding and logos
- Automate report generation with macros
4. Designing Your Access Database for CRM: Step-by-Step
Building an access database for CRM from scratch requires planning. A poorly designed database can lead to data redundancy, inconsistency, and performance issues. Follow these steps to create a solid foundation.
Step 1: Define Your Business Requirements
Before opening Access, ask: What do you want to track? Who will use the system? What reports do you need? For example, a consulting firm might need to track client projects, meeting notes, and billing status. A retail business might focus on purchase history and loyalty points.
- List all data entities (e.g., customers, orders, agents)
- Identify relationships between entities
- Determine reporting and automation needs
Step 2: Plan Your Table Structure
Use entity-relationship modeling to design your tables. Normalize your data to eliminate duplication. For example, instead of storing customer address in every order record, create a separate Customers table and link it to the Orders table via a CustomerID.
Common tables in a CRM Access database include:
- tblCustomers
- tblContacts
- tblInteractions (calls, emails, meetings)
- tblLeads
- tblProducts
- tblUsers (for team members)
Step 3: Build and Test the Database
Start by creating tables with appropriate fields and data types. Set primary keys and enforce referential integrity. Then, create relationships between tables using the Relationships tool. After the structure is in place, add sample data and test queries and forms.
“A well-designed database is like a well-organized filing cabinet—everything has its place.” — Database Design Best Practices, GCF Global
5. Enhancing Your Access Database for CRM with Automation
One of the most powerful features of Access is its ability to automate repetitive tasks. This transforms your access database for CRM from a static repository into a dynamic business tool.
Using Macros for Simple Automation
Macros allow you to automate actions without writing code. For example, you can create a macro that opens a specific form when the database starts, or one that exports a report to PDF and emails it.
- Create a macro to send follow-up reminders
- Automate data import from Excel or CSV
- Run validation checks on data entry
Leveraging VBA for Advanced Functionality
For more complex automation, Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is the way to go. With VBA, you can write custom functions, interact with other Office applications, and even integrate with Outlook for email automation.
Example: A VBA script can scan the Interactions table and automatically flag customers who haven’t been contacted in 30 days, then generate a task list for the sales team.
Integrating with Outlook and Excel
Access can seamlessly integrate with other Microsoft Office tools. You can pull customer data from Access into Outlook to personalize emails, or export sales data to Excel for advanced analysis.
- Link Access tables to Outlook contacts
- Use Excel PivotTables on exported data
- Automate monthly reporting with scheduled exports
6. Security and Maintenance of Your Access Database for CRM
While Access is powerful, it’s not immune to risks. As your CRM database grows, so does the need for proper security and maintenance.
Securing Your Data
Access databases are typically stored as .accdb files, which can be copied or deleted easily. To protect sensitive customer information, implement security measures such as password protection, user-level security (in older versions), and regular backups.
- Set strong passwords for database access
- Split the database into front-end (forms) and back-end (tables)
- Store the back-end on a secure network drive
Regular Backups and Compact & Repair
Access databases can become fragmented over time, leading to slower performance. Use the built-in “Compact & Repair” tool regularly to optimize file size and improve speed. Always keep multiple backup copies—preferably in different locations.
“Backups are not optional. They’re your safety net when things go wrong.” — IT Pro Magazine
Handling Multi-User Access
When multiple users access the same database, conflicts can arise. To avoid data corruption, split the database so each user has their own front-end copy linked to a shared back-end. This reduces network traffic and improves stability.
access database for crm – Access database for crm menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Use database splitting for team environments
- Limit concurrent edits to critical records
- Monitor performance on shared networks
7. Limitations and When to Upgrade from Access Database for CRM
While an access database for CRM is powerful for small operations, it has limitations. Recognizing when to upgrade is crucial for long-term success.
Scalability Issues
Access is not designed for large-scale applications. It has a 2GB file size limit, and performance degrades with hundreds of concurrent users. If your business grows rapidly, you may hit these limits quickly.
- File size capped at 2GB
- Limited support for high-concurrency environments
- No native cloud hosting (without third-party tools)
Data Integrity and Recovery
Unlike enterprise databases, Access lacks advanced transaction logging and rollback features. If the database becomes corrupted, recovery can be difficult. This makes it less suitable for mission-critical applications.
When to Consider a Full CRM System
If you find yourself spending more time managing the database than using it, or if your team is spread across locations, it may be time to move to a cloud-based CRM like Salesforce or Zoho CRM. These platforms offer mobile access, real-time collaboration, and robust integration capabilities.
“Access is a great starting point, but growth demands evolution.” — Small Business Trends
8. Real-World Examples of Access Database for CRM in Action
Theoretical knowledge is valuable, but seeing how others use an access database for CRM brings it to life. Let’s look at a few real-world scenarios where Access has made a tangible impact.
Case Study: Local Marketing Agency
A boutique marketing agency with 10 employees used Access to manage client campaigns, track deliverables, and log communication. By creating a custom CRM, they reduced missed deadlines by 40% and improved client satisfaction scores.
- Used forms for campaign intake
- Automated status update emails via VBA
- Generated monthly performance reports
Non-Profit Organization Tracking Donors
A non-profit used Access to track donor history, pledge fulfillment, and event attendance. The database helped them identify top donors and personalize outreach, increasing annual donations by 25%.
Freelance Consultant Managing Clients
A freelance business consultant built a lightweight CRM in Access to manage client onboarding, session notes, and invoicing. The system integrated with Outlook to schedule meetings and send reminders, saving 5+ hours per week.
9. Best Practices for Maintaining Your Access Database for CRM
Even the best-designed database can fail without proper maintenance. Follow these best practices to keep your access database for CRM running smoothly.
Document Your Database Structure
Create a data dictionary that explains each table, field, and relationship. This is invaluable for onboarding new team members or troubleshooting issues.
- Record field descriptions and data types
- Map out table relationships visually
- Keep a change log for updates
Train Your Team
Ensure all users understand how to enter data correctly and use forms and reports. Poor data entry can lead to inaccurate insights and wasted time.
Monitor Performance and Usage
Regularly review how the database is being used. Are certain queries slow? Are users bypassing forms to edit tables directly? Address issues early to prevent bigger problems.
“A CRM is only as good as the data it contains—and the people who use it.” — Harvard Business Review
10. Future-Proofing Your Access Database for CRM
Technology evolves fast. While Access remains a solid tool, future-proofing your CRM strategy ensures long-term success.
Plan for Migration
Design your Access database with migration in mind. Use standard data formats and avoid proprietary features that won’t transfer easily. This makes it simpler to move to a SQL-based system or cloud CRM later.
Explore Hybrid Solutions
You don’t have to abandon Access entirely. Some businesses use Access as a front-end for SQL Server databases, combining the ease of Access with the power of enterprise-grade backend storage.
Stay Updated on Microsoft’s Roadmap
Microsoft continues to support Access, but the focus is shifting toward cloud solutions like Power Apps and SharePoint. Stay informed about new features and consider how they might enhance your current setup.
- Explore Power Automate for workflow automation
- Use Power BI to visualize CRM data
- Consider migrating to Microsoft Dataverse for scalability
What is an access database for CRM?
An access database for CRM is a customer relationship management system built using Microsoft Access. It allows businesses to store, manage, and analyze customer data through a customizable, desktop-based database environment.
Can I use Access as a CRM system?
Yes, especially for small to mid-sized businesses. Access provides the tools to create a fully functional CRM with tables for customers, interactions, and sales tracking, along with forms, queries, and reports for usability.
Is Microsoft Access still relevant for CRM?
Yes, for specific use cases. While not suitable for large enterprises, Access remains a cost-effective, flexible solution for teams needing a simple, customizable CRM without the complexity of enterprise software.
How do I secure my Access CRM database?
Secure it by splitting the database, storing the back-end on a secure server, using strong passwords, and performing regular backups. Limit user permissions and avoid storing sensitive data in plain text.
When should I upgrade from Access to a full CRM?
Consider upgrading when you exceed 2GB of data, have more than 10-15 concurrent users, need mobile access, or require advanced automation and integration with other business tools.
An access database for CRM is more than just a data storage tool—it’s a strategic asset for small businesses looking to build stronger customer relationships without breaking the bank. From cost savings to customization, Access offers a powerful starting point. However, understanding its limitations and planning for the future ensures your CRM evolves with your business. Whether you’re a solo entrepreneur or a growing team, leveraging Access wisely can set the foundation for long-term success.
access database for crm – Access database for crm menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: